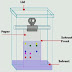
Column Chromatography is basically a term used
for the separation of compounds from a substance. This procedure proves to be
very useful when the compounds are available in the substance in very small
amount and hence it becomes very difficult to distinguish them from other. This
method is also used when those small amount of mixtures present in the
compounds have almost same physical or chemical properties. Chromatography is
said to be the best and the most convenient method for separation. The method
to be adopted in the separation process in chromatography depends on the
distribution of components in a mixture during the fixed or stationary and the
mobile or moving phase. The stationary phase is said to be the column of
absorbent, which can be a paper or a thin layer of any type of absorber on a
glass plate or any other thing through which the mobile phase can pass on.
The mobile phase can be of liquid or
gas. When the stationary phase of a solid takes place in a column it is said to
be column chromatography. Column chromatography is said to be one of the best
and the most useful method of separation and purification of any solid or
liquid substance. It is also said as a solid liquid method of separation where
the solid is said to be the stationary phase and liquid is said to be the
mobile phase. Column chromatography works on the objective based on the
differential absorption of substance based on the capacity of the absorbent.
Some of the common absorbents used in column chromatography are calcium
carbonate, magnesia, starch, alumina, silica and many more. One the contrary
the solvent is selected according to the nature of solvent as well as the
absorbent.